Defining roles and managing access control are critical steps in protecting an organization’s digital assets. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) simplifies this process by assigning permissions based on user roles, ensuring the right people have the right access at the right time. In this article, we will focus on how to effectively implement RBAC, streamline access management, and enhance overall security without adding unnecessary complexity.
How RBAC Regulates Access
Imagine someone logging into your computer system – what they can do depends entirely on the role they have. In RBAC, a role represents a group of users who share certain attributes, such as:
- The department they belong to
- Their work location
- Their position within the organisation
- Their specific job tasks
Once roles are defined, you can assign permissions to them, including:
- Access – What the user can view?
- Operations – What actions they can perform, like reading, writing, creating, or deleting files
- Sessions – When and for how long they can log in, including login duration and expiration
By structuring access this way, RBAC ensures users only have the permissions they need, improving security while simplifying administration.
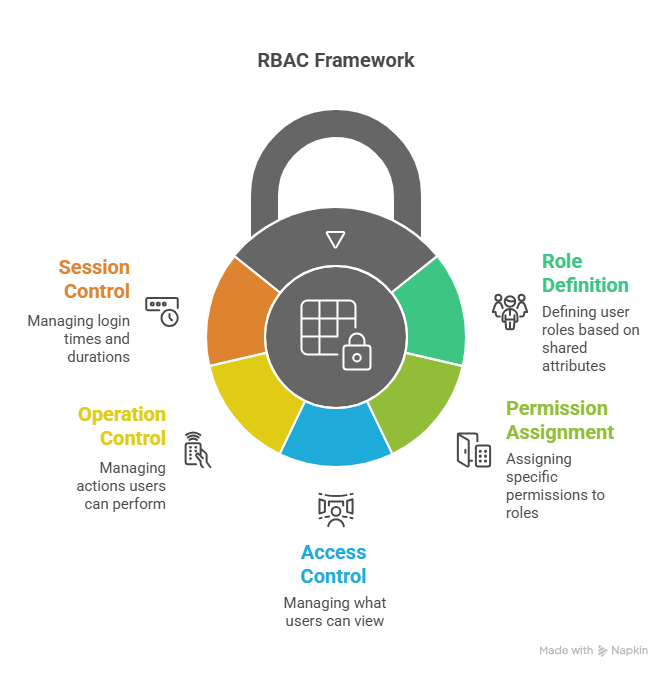
The RBAC methodology
By granting each role only the permissions required for their tasks, the RBAC methodology minimizes unnecessary access, reduces potential attack surfaces, and enhances the organization’s overall security framework. It is based on three primary rules that govern access to secured systems:
1. Role assignment:
A user can only perform an action if they have the correct role. Roles can be assigned by an administrator or chosen by the user trying to perform the action.
2. Role authorization:
Role authorization ensures that users can only take on roles they are permitted to hold. A user must receive approval from an administrator before assuming a role.
3. Permission authorization:
A user is allowed to perform an action only if their assigned role grants them the necessary permissions.
Best practices for implementing RBAC
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) successfully requires a structured approach to ensure users have the right access while minimizing security risks. Following these best practices can help organizations deploy RBAC efficiently and securely:
- Define clear roles:
Establish roles based on job functions, departments, or responsibilities to ensure each user has access only to what they need. Clear role definitions prevent confusion and make it easier to assign permissions consistently.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege:
Grant users only the permissions necessary to perform their tasks. This reduces the risk of accidental or malicious misuse of system resources.
- Centralize role management:
Use a centralized system to manage roles and permissions, making oversight and updates easier. Centralized management simplifies audits and ensures that policies and access rights are enforced consistently throughout the organization.
- Regularly review access rights:
Periodically audit roles and permissions to remove outdated or unnecessary access. Regular reviews help maintain security and ensure compliance with internal policies or regulations.
- Document roles and permissions:
Maintain clear records of role definitions and associated permissions for accountability and compliance. Proper documentation also helps in onboarding new employees and troubleshooting access issues.
- Train users and administrators:
Ensure all stakeholders understand RBAC processes and their responsibilities. Training promotes proper usage and reduces errors that could lead to security vulnerabilities.
Benefits of implementing RBAC
Implementing Role-Based Access Control brings significant advantages to the organizations. By assigning permissions based on roles, RBAC enhances security by limiting access to sensitive resources and reducing the potential attack surface. It also simplifies access management, making it easier for IT teams to control, audit, and adjust user permissions. Additionally, RBAC supports compliance with regulatory requirements, ensures operational efficiency, and reduces the risk of human error by granting users only the access they need to perform their tasks.
Overall, RBAC provides a structured, scalable, and secure framework for managing access in complex IT environments.
If your organization is looking for a trusted IAM partner to enhance your cybersecurity resilience and support scalable, long-term compliance, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us. We are here to help you turn information security into a true business advantage.

