The growing trend of remote work has reshaped how businesses operate and how employees access critical company resources. While remote work offers flexibility and increased productivity, it also brings significant security challenges. One of the most effective ways to safeguard corporate data and applications is through Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems. In this article, we’ll share how businesses can implement secure access for remote employees using IAM solutions and best practices.
The Importance of IAM in Securing Remote Access
Identity and Access Management encompasses the processes, policies, and technologies that control user identities and manage their access to organizational resources. It ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive systems and data, based on their identity and role within the company. With the growing number of remote employees, it has become crucial for businesses to adopt IAM solutions to reduce the risks associated with unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations.
IAM plays a critical role in securing remote access by authenticating users, ensuring that only legitimate individuals can access business systems. It also enforces role-based access control, which limits access to sensitive information based on the employee’s role within the organization. To further secure login processes, IAM replaces traditional password systems with more secure methods such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Additionally, IAM helps monitor who is accessing information and when, allowing businesses to detect and respond to any suspicious activity. Compliance with regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, is also facilitated by IAM systems.
Key steps to implement secure access with IAM for remote employees
To implement secure access with IAM for remote employees, organizations need to adopt a variety of strategies and technologies that enhance the overall security and ensure the proper control of remote access. This includes utilizing robust authentication methods and enforcing strict access policies based on employee roles. By integrating these practices, organizations can safeguard sensitive data and maintain a secure remote working environment:
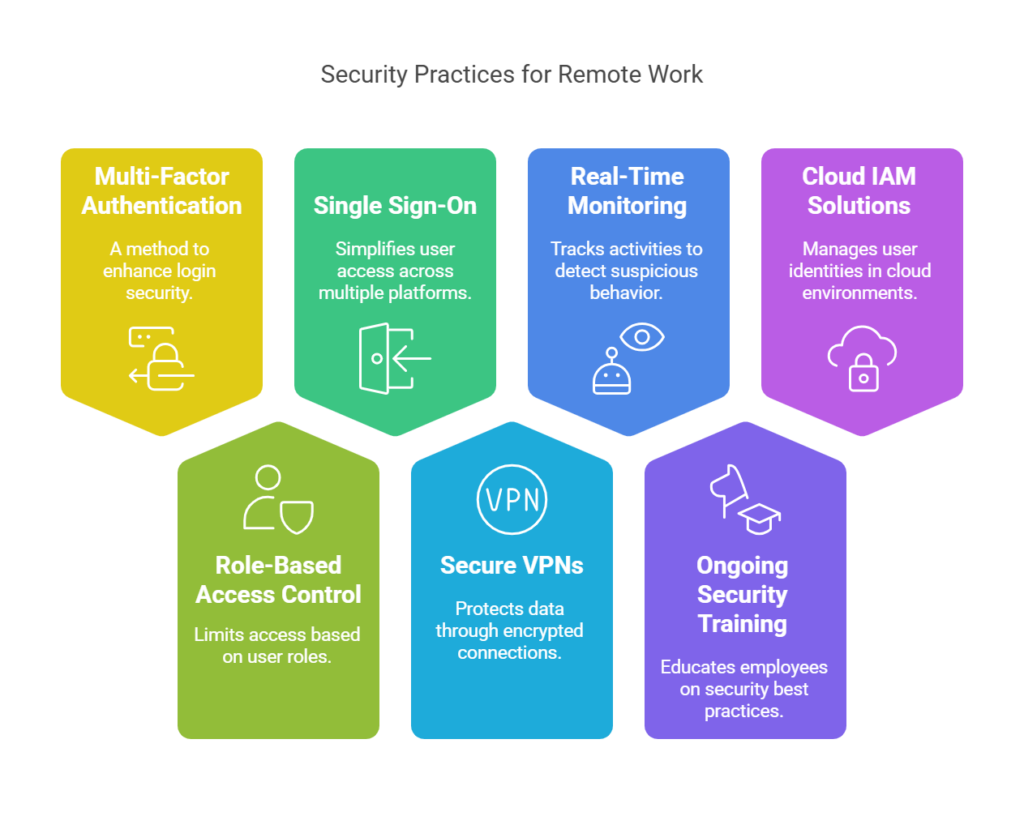
1. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive company data, especially when employees are accessing resources from various locations and devices. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide more than just a password.
MFA typically involves two or more of the following factors:
- Something you know: A password or PIN.
- Something you have: A mobile phone, smart card, or hardware token.
- Something you are: Biometrics, such as a fingerprint or facial recognition.
By implementing MFA, businesses can greatly reduce the chances of unauthorized access due to stolen or weak passwords, which is a common vulnerability in remote work environments.
2. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures that remote employees can only access the systems and data that are necessary for their job functions. By implementing RBAC, businesses can apply the principle of least privilege, meaning that employees are granted the minimum access required to perform their tasks.
For example: A marketing employee may only need access to content management systems and social media platforms. An IT administrator may require access to servers, networks, and cloud infrastructure. By clearly defining roles and associated permissions, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems, particularly when working remotely.
AI generated image
3. Enable Single Sign-On (SSO)
Managing multiple passwords across different applications can be difficult for remote employees, leading to poor password hygiene or the reuse of weak passwords. Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies this process by allowing employees to access multiple systems and applications with a single set of login credentials.
SSO improves both security and user experience by:
- Reducing the number of passwords employees need to remember.
- Enabling a faster and more seamless login process.
- Making it easier for businesses to enforce strong authentication policies (e.g., MFA).
When remote workers can easily and securely access the tools they need, their productivity increases, and the likelihood of security breaches decreases.
4. Use Secure Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
When remote employees access corporate systems, it’s essential to ensure that their connections are encrypted and secure. One of the most common methods of achieving this is by using a VPN (Virtual Private Network). A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between the employee’s device and the company’s internal network, protecting data from being intercepted by third parties. Businesses should require remote workers to use a VPN when accessing sensitive systems or data, especially when working over unsecured public networks (e.g., coffee shop Wi-Fi). Additionally, IAM can help ensure that VPN access is only granted to authenticated users with the appropriate permissions.
5. Monitor Access and Activity in Real-Time
For remote workers, monitoring access to sensitive data and systems is critical in detecting potential security risks. An IAM system should provide real-time logging and reporting of user activity, including:
- Logins and logouts
- Application access
- Changes to sensitive data
By monitoring these activities, businesses can identify unusual behavior (e.g., an employee accessing data they shouldn’t) and take prompt action to mitigate any security threats. Advanced IAM systems can also use machine learning to analyze user behavior and detect anomalies that may indicate a potential breach or compromise.
6. Provide Ongoing Security Training
Despite the best security measures, human error remains one of the biggest vulnerabilities in remote work environments. Employees must be educated on the risks associated with remote work and the importance of following security protocols.
Training should cover topics such as:
- Recognizing phishing attempts
- Secure password management practices
- How to securely access company resources from different devices
- The importance of using secure networks
By investing in security training for remote workers, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches due to negligence or lack of awareness.
7. Leverage Cloud-Based IAM Solutions
Many businesses are shifting to cloud-based solutions to accommodate the growing remote workforce. Cloud-based IAM solutions offer flexibility and scalability, enabling companies to manage secure access for remote employees from anywhere. Cloud IAM solutions typically come with built-in security features, such as automated updates, disaster recovery, and integration with various cloud applications. They can also scale easily as the organization grows, ensuring that the same level of security is maintained regardless of the size of the remote workforce.
As the trend of remote work continues to grow, businesses must adopt robust Identity and Access Management strategies to ensure the secure access of remote employees to critical systems and data. By implementing multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, single sign-on, VPNs, real-time monitoring, and cloud-based IAM solutions, organizations can protect sensitive information from potential threats and maintain a secure work environment, no matter where their employees are located. With the right IAM practices in place, businesses can enjoy the benefits of a remote workforce while minimizing security risks and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
